AWS WAF
1. Introduction
AWS WAF is part of the suite of AWS networking security services that protect applications against threats targeting the application layer. It is designed to prevent exploits such as cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and other common vulnerabilities. Originally introduced in 2015, the service was re-engineered in 2019 to provide enhanced functionality, improved performance, and greater ease of use. With the release of the new version, AWS recommends that existing users of WAF Classic migrate to the updated service to take full advantage of its modern capabilities, including automated updates, scalable configurations, and more flexible rule definitions.
2. Core Features and Benefits
AWS WAF offers several key features and benefits that simplify web application protection while ensuring robust security controls.
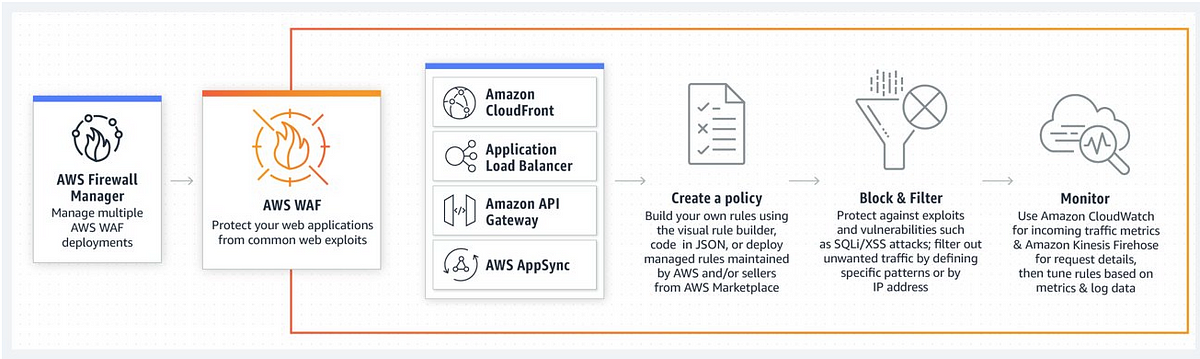
2.1. Managed Rules and Quick Deployment
One of the primary benefits of AWS WAF is the availability of managed rules. These rules are maintained by AWS and trusted third-party vendors, allowing customers to quickly deploy security measures without the need for extensive custom rule development. Managed rules cover a wide range of known threats, including the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, and enable rapid protection from new vulnerabilities as they emerge. This managed rule set significantly reduces the time and expertise required to secure web applications.
2.2. Web ACL Capacity Units (WCU)
In the updated version of AWS WAF, capacity is measured in Web ACL Capacity Units (WCUs) rather than a simple rule count. This capacity-based pricing model ensures that users pay for the processing power required to evaluate their rules. The WCU model offers a more granular approach to managing resource usage, allowing organizations to scale their WAF configurations in line with their security needs while maintaining predictable performance and cost profiles.
2.3. JSON-Based Rule Configuration
AWS WAF supports rule configuration through JSON documents, enabling users to import or update rules without relying solely on the AWS Management Console. This JSON-based configuration approach facilitates automation and integration with continuous deployment pipelines, offering greater flexibility in managing security policies programmatically. By supporting a declarative configuration format, AWS WAF simplifies the process of versioning, auditing, and replicating security rules across multiple environments.
2.4. Logical Rule Combinations
A significant enhancement in the new AWS WAF is the ability to combine multiple rules using logical operators. Users can now create complex security policies by constructing logical conditions such as "A and B, not C." This flexibility allows for more granular control over traffic filtering and better alignment with specific application requirements. Previously, combining multiple rules was either cumbersome or not supported; the updated functionality enables administrators to tailor their security posture with precision.
3. Deployment Targets: CloudFront, ALB, API Gateway, and AppSync
AWS WAF is designed to be seamlessly integrated with various AWS services. It can be deployed in front of:
- Amazon CloudFront: Protecting content delivered via a global content delivery network.
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): Securing traffic directed to scalable web applications.
- API Gateway: Safeguarding RESTful APIs against malicious requests.
- AppSync: Protecting GraphQL APIs used by modern web and mobile applications.
This versatility eliminates the need for additional software or complex configurations such as DNS modifications, SSL/TLS certificate management, or reverse proxy setups. By directly associating AWS WAF with these resources, organizations can rapidly deploy robust web application protection with minimal operational overhead.
4. Web ACLs: Structure and Functionality
At the core of AWS WAF is the Web Access Control List (Web ACL). A Web ACL is a collection of rules that define the conditions under which requests are allowed or blocked. Key elements of Web ACLs include:
- Traffic Inspection: Rules within a Web ACL inspect various components of HTTP requests, including IP addresses, HTTP headers, request bodies, URLs, and query strings.
- Rate-Based Rules: These rules help mitigate automated threats by limiting the number of requests allowed from a single IP address within a specified time frame.
- Size Constraints: Administrators can set limits on the size of requests, ensuring that unusually large or malformed requests, which might indicate an attack, are blocked.
- Evaluation Limits: For performance reasons, AWS WAF currently inspects only the first 8,192 bytes of an HTTP request. This limitation is important to consider when designing rules for applications that may generate larger requests.
By aggregating these capabilities, Web ACLs provide a structured and efficient mechanism to enforce complex security policies tailored to the specific needs of each web application.
5. Protecting Against Common Attacks
AWS WAF is engineered to protect applications from a variety of common attack vectors, particularly those targeting layer seven vulnerabilities. The key protections include:
- IP Whitelisting and Blacklisting: Administrators can dynamically manage lists of allowed or blocked IP addresses, whether IPv4 or IPv6, to restrict access from untrusted sources.
- Header, Body, and URL Inspection: Rules can be crafted to scrutinize HTTP headers, body content, and URL strings for malicious patterns or unwanted data.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Protection: AWS WAF can detect and block attempts to inject malicious scripts into web pages, thereby protecting user data and preventing script execution on the server.
- SQL Injection Prevention: By analyzing input fields and query strings, AWS WAF identifies and prevents SQL injection attacks that could compromise database integrity.
- Geographic Matching: This feature enables administrators to allow or block traffic based on the geographic origin of the request, useful for enforcing regional access policies.
- Rate Limiting: By applying rate-based rules, AWS WAF can detect and mitigate denial-of-service attacks or bot-driven traffic surges, ensuring continued availability of the web application.
Each of these measures contributes to a comprehensive defense strategy against both common and emerging threats.
6. Integration with AWS Services and Third-Party Rules
AWS WAF is deeply integrated with various AWS services and supports third-party rule sets available through the AWS Marketplace. This integration facilitates:
- Seamless Policy Management: AWS-provided core rules address the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities and are continually updated to respond to emerging threats (including new CVEs). This means that once deployed, the rules adapt to provide ongoing protection without requiring manual intervention.
- Third-Party Enhancements: For organizations with specific security requirements, third-party vendors offer specialized rule sets that can be imported into AWS WAF, further enhancing its capabilities.
- Automated Updates: The managed rule sets are designed to automatically update as new vulnerabilities are discovered, ensuring that the application remains protected against the latest threats.
This ecosystem approach ensures that AWS WAF remains a future-proof solution that can evolve with the security landscape.
7. Monitoring and Response Mechanisms
Effective security is not only about preventing attacks but also about monitoring and quickly responding to potential threats. AWS WAF provides robust monitoring and response capabilities, including:
Real-Time Rule Propagation: AWS WAF is designed for rapid deployment and propagation of new rules. Once a rule is added to a Web ACL, it is typically active within one minute. For services such as CloudFront, which operate out of multiple global locations, rule updates propagate across all eight edge locations, ensuring that the protection is applied universally and without delay.
Handling Blocked Requests (403 Forbidden): When AWS WAF detects a request that violates one of the defined rules, it blocks the traffic and returns an HTTP 403 Forbidden status code. This immediate response serves as a clear indication that the request has been identified as malicious. The 403 status is a standard part of web security, ensuring that unauthorized or potentially harmful requests do not reach the protected application.
8. Best Practices
To maximize the effectiveness of AWS WAF, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Leverage Managed Rules: Utilize AWS managed rule sets for rapid deployment and ongoing protection. These rules are maintained by AWS and third-party vendors, ensuring that they are always up-to-date.
- Adopt JSON-Based Configurations: Take advantage of the JSON-based rule configuration to integrate AWS WAF into automated deployment pipelines, ensuring consistent and reproducible security configurations.
- Utilize Logical Rule Combinations: Build complex security policies by combining rules logically. This approach allows for precise control over which types of requests are permitted or blocked.
- Implement Rate-Based Rules: Use rate limiting to defend against denial-of-service attacks and bot traffic, ensuring that the application remains available under heavy load.
- Regularly Update IP Lists and Size Constraints: Maintain dynamic IP whitelist/blacklist configurations and appropriate size constraints to address evolving threats and changing traffic patterns.
- Monitor and Audit: Continuously monitor traffic and audit rule performance to ensure that the Web ACLs are effectively mitigating risks and to fine-tune rules as needed.
9. Conclusion
AWS WAF is a critical component in the defense of modern web applications, offering a powerful combination of ease-of-use, flexible configuration, and robust security controls. Its evolution from WAF Classic to the current iteration reflects a significant improvement in the ability to manage and deploy web application security. By incorporating managed rules, Web ACL Capacity Units, JSON-based configurations, and logical rule combinations, AWS WAF provides a comprehensive, scalable, and adaptive solution for protecting against a wide range of application-layer attacks.