AWS Database Migration Service
1. Introduction
Organizations frequently need to move large datasets between different database engines or environments, whether from on-premises to the cloud or between cloud-based databases. Key challenges include:
- Minimizing Downtime: Mission-critical applications must remain available during the migration.
- Ensuring Data Integrity: Data must be consistent and accurate throughout the transfer.
- Handling Schema and Engine Differences: Migrating between different database engines (heterogeneous migrations) often requires schema and code transformations.
- Network Bandwidth Constraints: Large-scale data transfers can be impacted by network limitations.
AWS DMS addresses these challenges with features such as continuous replication (via Change Data Capture or CDC), automated failover, and secure, incremental updates.
2. Overview of AWS Database Migration Service
AWS DMS is a fully managed service that copies data from a source to a target database with near-zero downtime. It supports both one-time migrations and ongoing replication, ensuring the source database remains fully operational during the process. AWS DMS is built for reliability—it automatically recovers from many common failures—and is designed for both homogeneous migrations (e.g., Oracle to Oracle) and heterogeneous migrations (e.g., Microsoft SQL Server to Amazon Aurora).
Key points include:
- Near-Zero Downtime: Continuous data replication minimizes service disruption.
- Flexibility: Supports a broad range of database engines and deployment scenarios.
- Cost-Effective: Operates on a pay-as-you-go model, with options to scale using either provisioned instances or serverless capacity.
3. Key Features and Benefits
Minimal Downtime
AWS DMS continuously replicates data changes from the source to the target database, allowing you to perform migrations with little or no interruption.
Broad Database Support
AWS DMS supports over 20 different database engines—including Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MongoDB, and more—for both source and target roles. This makes it a versatile tool for a variety of migration scenarios.
Flexible Deployment Options
You can choose between:
- Traditional Replication Instances: Managed on Amazon EC2.
- Serverless Option: Automatically scales based on demand so you only pay for what you use.
Resiliency and Self-Healing
The service monitors connectivity and system health. In case of failures, AWS DMS automatically restarts the process from the point of failure to maintain data integrity.
Integrated Assessment Tools
Tools such as AWS DMS Fleet Advisor help inventory and assess on-premises databases, while the AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) assists with converting database schemas during heterogeneous migrations.
Security
Data is encrypted in transit (using SSL) and at rest (with AWS Key Management Service), ensuring that your sensitive information remains protected throughout the migration.
4. How AWS DMS Works
AWS DMS orchestrates the migration through three main components:
-
Endpoints:
- Source and Target Endpoints are configured with details such as engine type, server name, port, encryption settings, and credentials. They establish secure connections for data transfer.
-
Replication Instance:
- A managed Amazon EC2 instance (or serverless resource) runs the replication software that extracts, optionally transforms, and loads the data.
- Different instance types (e.g., T2/T3 for development/testing, C4, R4, R5 for production workloads) can be chosen based on performance needs.
-
Replication Tasks:
- These tasks specify what data to move and how. You can choose from:
- Full Load: Migrates all data in one go.
- Full Load + CDC: Performs an initial full load and then applies ongoing changes.
- CDC Only: Replicates only the incremental changes.
This flexibility allows you to handle one-time migrations or maintain continuous synchronization between the source and target.
- These tasks specify what data to move and how. You can choose from:
6. Supported Sources and Targets
AWS DMS supports a wide variety of databases as both sources and targets:
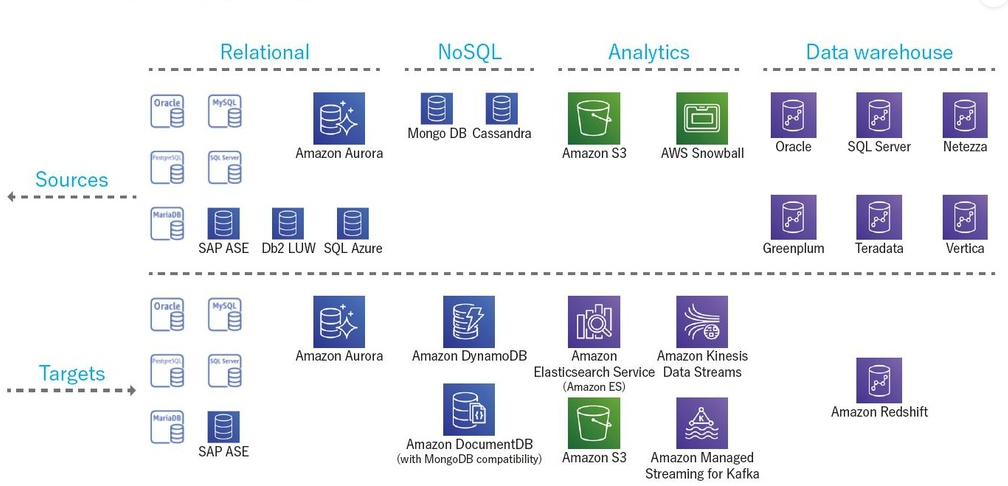
Sources
- On-Premises or EC2-Hosted Databases: Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SAP, DB2.
- Cloud Databases: Amazon RDS (including Aurora), Azure SQL Database.
- Data Files: Amazon S3 (using data files as a source).
- DocumentDB (MongoDB-compatible): For MongoDB-based sources.
Targets
- On-Premises or EC2-Hosted: Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SAP.
- AWS Managed Services: Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon Redshift, Amazon DynamoDB.
- Other AWS Services: Amazon S3, OpenSearch Service (formerly Elasticsearch), Kinesis Data Streams, DocumentDB (MongoDB-compatible).
Note: Some AWS services (e.g., Amazon Redshift, Kinesis Data Streams, OpenSearch Service) can only act as targets.
7. AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT)
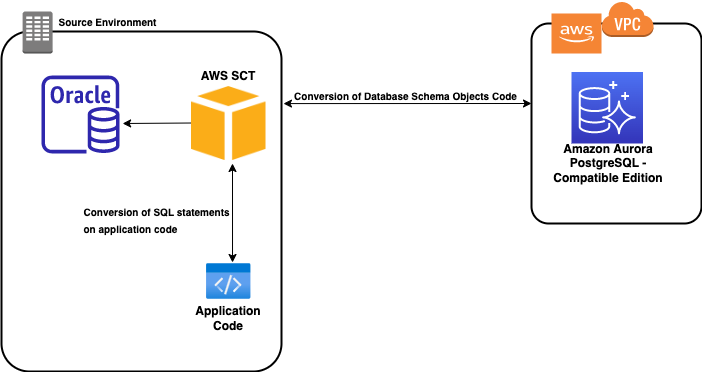
The AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) is a utility designed to simplify database migration by automating the conversion of your source database schema and related code (like stored procedures, functions, and triggers) to a format compatible with your target database. This tool is particularly useful when migrating from commercial databases (such as Oracle or SQL Server) to open-source databases (such as PostgreSQL or MySQL) or to AWS-managed databases like Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora. It analyzes the source schema, identifies compatibility issues, and generates a migration assessment along with conversion scripts that you can then customize as needed.
In addition to schema conversion, SCT helps reduce manual effort by pinpointing areas where code might need adjustments, thereby streamlining the overall migration process and lowering the risk of errors. It supports a variety of database engines and can be a critical component in modernizing legacy applications while taking advantage of AWS's scalable infrastructure.
8. Combining AWS Snowball and DMS
For very large migrations where network bandwidth is a constraint, AWS Snowball (or Snowball Edge) devices provide an offline method to transfer petabytes of data securely. The typical hybrid approach is:
-
Bulk Transfer:
Use AWS Snowball to transfer a large volume of data to an Amazon S3 bucket. -
Final Sync:
Use AWS DMS to load data from the S3 bucket into the target database and then apply any incremental changes (via CDC) that occurred while the data was in transit.
This method ensures efficient bulk transfer combined with near real-time synchronization.
9. Conclusion
AWS Database Migration Service is a versatile and robust solution for migrating databases to AWS. By automating many of the traditionally complex and time-consuming tasks—such as capacity planning, data replication, and infrastructure management—AWS DMS enables both straightforward and complex migrations with minimal downtime and high reliability.